Importance of Material Selection
Importance of Material Selection
For a regulator with a long "economic life", the use of "correct" materials is of great importance. Now, let's examine how the "correct" material selections should be for certain structural parts of the regulator.
B.1.Body and Covers
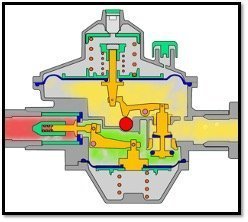
The parts that carry the pressure and external mechanical loads in the regulator and are also exposed to environmental factors with the highest intensity are the covers that close the body and regulation stages. Therefore, material selection is very important here. The standards allow the use of many materials. However, due to structural and economic reasons, the body and covers are made of Aluminum alloys and ZAMAK alloys. It can give good results with correct use in both materials.
However, aluminum material needs more protection against corrosion compared to zame. For this reason, painting aluminum regulators with "electrostatic powder paint" is a factor that increases the "economic life".
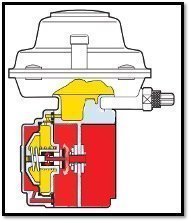
On the other hand, if the outer covers are directly exposed to gas pressure, we mentioned the necessity of extra protection of them in the corrosion section of our other article. For this reason, the protection of regulators with this type of design with "paint" is a necessity for a long "economic life" and safe use. For cover designs that do not contain pressure, as in the picture on the right, there will be no need for extra protection with "paint" as this is not a risk.
B.2.Springs
Springs are the most important parts that stabilize the output pressure of the regulator and ensure that the pressure remains the same throughout the “economic life”. Therefore, the choice of spring material is also important for a long "economic life".
Springs made of spring steel can be protected for a certain period of time by coating on them. However, this is a type of protection that can disappear in a very short time depending on the quality and thickness of its coating and the environment it is exposed to. Especially the springs exposed to moisture lose the coating on them within a few years and become "bare" and "unprotected". As a result, the wall thicknesses decrease rapidly with corrosion. This prevents the regulator from giving the required pressure and flow, leading to failure notifications.
For these reasons, it is necessary to use springs made of "stainless" material for a long "economic life" and a stable regulation pressure.
B.3.Plastic Parts
For economic reasons, it is possible to make some parts of the regulators plastic. However, the use of plastic parts should be limited by evaluating their effects on "safe" use and long "economic life".
The fact that the mechanical properties of plastic parts change with temperature should be taken into account. Especially when this situation is combined with high pressure, it creates a high risk in terms of "safety" and "lifetime". For this reason, plastic should not be used “absolutely” in the manufacture of parts that participate in regulation and safety. Plastic parts should not be used in areas that come into contact with gas and are exposed to differential pressure. Plastic parts must not be threaded. Because the micro cracks that occur during this process can cause the part to break or crack over time and cause leaks.
On the other hand, it should be kept in mind that in case of accidental service box fires, regulators whose internal parts melt may cause the gas to pass to the outlet or come out of the regulator body.
In short, for a safe and long-lasting use, plastic parts can be used in a very limited space, for example on the atmospheric pressure side as backing plates for diaphragms. Other uses will not be “safe” and long-lasting.
B.4.Parts that participate in closure and regulation
One of the most important elements of the "economic longevity" is to ensure that the "outlet pressure" remains within a certain range. Here again, material selection is very important. Especially considering the effect of internal corrosion on materials, the basic parts such as “orifice”, “plug”, “safety plug” that participate in the regulation must be made of “non-rusting” and “non-corroding” materials. Here too the basic correct material is MS58 brass types. It is possible to make these parts from "ZAMAK" or aluminum for cost advantage. However, they are not suitable for long-term use. In many international and national specifications (for example, İGDAŞ), this issue is particularly emphasized.


